Processed Fruit Market
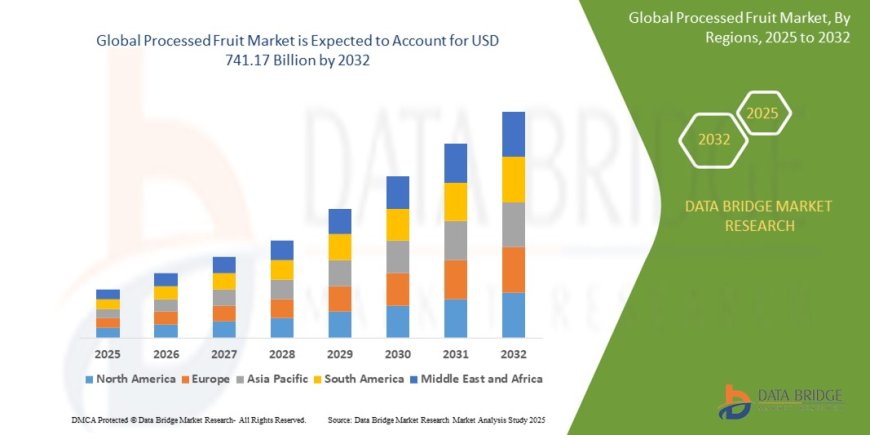
The global processed fruit market size was valued at USD 387.33 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 741.17 billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 8.45% during the forecast period
Processed fruits refer to fruits that have undergone treatments to alter their raw form for extended shelf life, convenience, and value addition. Common processing methods include freezing, drying, canning, juicing, pureeing, and making jams, preserves, or concentrates. The processed fruit market caters to diverse industries such as food and beverages, confectionery, bakery, dairy, and nutraceuticals.
Increasing consumer preference for ready-to-eat, convenient, and nutritious food options is fueling the processed fruit market growth. Processed fruits provide the nutritional benefits of fresh fruits while offering longer storage periods and ease of use. Rapid urbanization, changing lifestyles, and increasing demand for functional foods and beverages are major factors accelerating the consumption of processed fruits globally.
The processed fruit industry also supports sustainability by reducing fruit wastage through preservation and value addition. This is particularly important in regions with seasonal fruit production where surplus harvests can be processed and stored for off-season consumption.
The growing demand for natural and clean-label products is influencing processing technologies and ingredient choices. Processors aim to retain the sensory and nutritional attributes of fresh fruits while ensuring food safety and compliance with regulatory standards.
The Evolution
The processed fruit market has evolved considerably over the last century. Early methods of fruit preservation were primarily focused on simple drying and sugar-based preservation techniques such as jams and jellies. These traditional methods date back thousands of years but became more systematized with industrialization in the 19th century.
The invention of canning in the early 1800s revolutionized the fruit processing industry. Canning allowed fruits to be preserved in sealed containers and stored for months without spoilage. This enabled wider distribution of fruit products to areas beyond local production zones.
Freezing technology advanced significantly in the 20th century. Quick freezing methods developed in the 1930s allowed better preservation of the flavor, texture, and nutrients of fruits. Frozen fruits became popular for use in desserts, smoothies, and processed foods.
Juices and concentrates gained prominence with advances in extraction and filtration technologies. The global juice market, driven by health-conscious consumers, boosted demand for processed fruit derivatives. The rise of aseptic packaging further improved shelf life and product quality.
Freeze-drying emerged as a premium fruit processing technique preserving nearly all nutrients and flavor. It enabled lightweight, portable fruit snacks and ingredients, expanding product categories.
The late 20th and early 21st centuries saw increasing emphasis on minimal processing to maintain freshness and naturalness. Technologies like high-pressure processing (HPP) and pulsed electric fields (PEF) were introduced to enhance shelf life while preserving quality.
Digitalization, automation, and sophisticated quality control systems have optimized processing efficiency and traceability. Innovation continues in flavor enhancement, natural preservatives, and environmentally friendly packaging.
Market Trends
Consumers globally are embracing processed fruits as part of their daily diet due to convenience, nutritional benefits, and versatility. The rise of snacking culture has led to demand for dried fruit snacks, fruit bars, and bite-sized fruit treats.
Health and wellness trends drive the consumption of natural fruit juices, smoothies, and functional beverages fortified with processed fruit extracts. Clean label claims, non-GMO ingredients, and organic certifications are increasingly important.
Frozen fruits are witnessing strong growth as consumers prepare more meals at home. The surge in frozen fruit smoothies and dessert bases supports this demand. Frozen fruit blends combining multiple fruit types offer variety and enhanced nutrition.
E-commerce is transforming the distribution landscape. Consumers purchase frozen and dried fruits, fruit juices, and purees online for home delivery. Direct-to-consumer brands are leveraging digital platforms to offer customized fruit-based products.
Sustainability and food waste reduction are shaping sourcing and production. Farmers and processors collaborate to utilize surplus and imperfect fruits for processing rather than disposal. Circular economy practices and upcycling of fruit by-products into fibers, extracts, and natural colorants are gaining traction.
Product innovation includes blending fruits with superfoods, probiotics, and plant proteins to cater to functional food markets. Exotic and tropical fruits are gaining consumer attention as premium processed fruit ingredients.
Emerging markets in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa are experiencing rapid growth driven by rising incomes, urbanization, and westernization of diets. Local fruit varieties are also being processed to cater to regional preferences.
The COVID-19 pandemic shifted consumer behavior toward immune-boosting and natural products. Demand for vitamin C-rich fruit products such as citrus juices and acerola cherry extracts rose sharply. Consumers also increased their consumption of long shelf-life processed fruits due to stockpiling.
Regulatory focus on sugar content and labeling transparency is encouraging the development of reduced-sugar and no-added-sugar fruit products. Processors reformulate to meet these requirements while maintaining taste and functionality.
Challenges
Maintaining the nutritional quality of processed fruits is a key challenge. Many vitamins and antioxidants are sensitive to heat, oxygen, and light, leading to degradation during processing and storage.
Flavor retention is difficult, especially for heat-processed fruits. Off-flavors can develop due to enzymatic browning and Maillard reactions. Ensuring sensory appeal is essential for consumer acceptance.
Raw material variability due to seasonal, climatic, and geographic factors impacts product consistency. Processors must optimize formulations to accommodate these differences while maintaining quality.
Supply chain complexities arise from the perishability of fresh fruits and dependency on harvesting windows. Delays or disruptions can lead to raw material shortages or quality issues.
Regulatory compliance varies widely by country, complicating international trade. Adherence to maximum residue limits for pesticides, food safety standards, and labeling regulations requires extensive monitoring and certification.
Consumer concerns regarding added sugars, preservatives, and additives pose marketing challenges. Meeting demand for clean-label and natural processed fruit products while ensuring shelf stability requires innovation.
Sustainability challenges include water usage, energy consumption, and waste management during processing. Companies must adopt greener technologies to minimize environmental impact.
Price volatility of fresh fruits due to weather events, pests, and crop failures affects production costs and profit margins.
Competition from fresh fruits and alternative snack options requires constant product differentiation and marketing.
Food safety risks such as microbial contamination and mycotoxins require strict quality control measures.
Technological investments for advanced processing methods may be cost-prohibitive for small and medium enterprises.
Market Scope
The processed fruit market spans a wide range of product categories. These include canned fruits, frozen fruits, dried fruits, fruit juices and concentrates, purees and pulps, jams and jellies, fruit-based snacks, and fruit ingredients for industrial use.
Canned fruits are often used in desserts, bakery, confectionery, and ready meals. They offer long shelf life and convenience but face demand pressures due to consumer preference for fresh or minimally processed foods.
Frozen fruits are popular among consumers seeking fresh-like taste and nutrition. They find applications in smoothies, yogurt toppings, baking, and culinary use.
Dried fruits are consumed as snacks and used in cereals, trail mixes, and confectionery. They provide concentrated nutrients and energy with extended shelf life.
Fruit juices and concentrates serve beverage manufacturers and food formulators. They provide natural flavors, colors, and nutritional enrichment.
Purees and pulps are key ingredients in baby food, bakery fillings, and dairy products. They allow formulation flexibility and easy incorporation of fruit nutrition.
Jams, jellies, and preserves cater to retail and food service sectors. Traditional and low-sugar variants coexist to meet varied consumer needs.
Fruit-based snacks such as fruit bars, leathers, and freeze-dried pieces are gaining market share in health-conscious and on-the-go consumption segments.
Industrial users of processed fruit include bakeries, confectionery manufacturers, beverage producers, dairy companies, and nutraceutical formulators. They require consistent quality, customized specifications, and large volumes.
The processed fruit market includes both B2B and B2C sales channels. Retail, food service, and institutional buyers purchase bulk ingredients, while packaged consumer products reach supermarkets, specialty stores, and e-commerce platforms.
Geographically, North America and Europe are mature markets with high demand for premium, organic, and convenience processed fruit products. Asia-Pacific is the fastest growing region due to urbanization, rising disposable incomes, and expanding retail infrastructure.
Latin America and Africa represent emerging opportunities driven by local fruit availability, increasing awareness, and government support for value-added agriculture.
Market Size and Factors Driving Growth
The global processed fruit market was valued at approximately USD 70 billion in 2024 and is forecasted to reach USD 95 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 5.2%. Growth is propelled by increasing consumer demand for nutritious, convenient, and shelf-stable fruit products.
Demographic shifts such as urbanization and increasing working population enhance demand for ready-to-eat and on-the-go processed fruit products.
Health consciousness and nutritional awareness promote consumption of fruit juices, dried fruits, and fruit snacks rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
Technological innovations in processing and packaging improve product quality, shelf life, and consumer appeal. Aseptic packaging, vacuum drying, and HPP contribute to superior processed fruit products.
Rising disposable income in emerging economies enables higher spending on value-added and premium fruit products.
The expansion of organized retail and e-commerce facilitates wider product availability and consumer reach.
The growing use of processed fruits as ingredients in bakery, confectionery, dairy, and beverages stimulates demand for bulk fruit purees and concentrates.
Government initiatives promoting fruit processing and reducing post-harvest losses support market growth.
Increasing exports and international trade open new markets for processed fruit products.
The preference for natural and clean-label products drives innovation in additive-free and organic processed fruits.
Sports nutrition and functional food trends fuel demand for fruit-based energy bars, powders, and beverages.
Source: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-processed-fruit-market
Conclusion
The processed fruit market is a vibrant and expanding segment driven by changing consumer lifestyles, increasing health awareness, and technological progress. Processed fruits bridge the gap between fresh fruit nutrition and modern convenience, offering diverse applications across food, beverage, and nutraceutical industries.
Despite challenges related to quality preservation, regulatory complexity, and sustainability, the market outlook remains optimistic. Industry stakeholders are innovating in processing technologies, clean-label formulations, and sustainable sourcing to meet evolving consumer demands.
Growth opportunities are abundant in emerging markets, e-commerce, and functional product segments. Strategic collaborations between fruit growers, processors, retailers, and technology providers are key to harnessing the full potential of the processed fruit market.
Processed fruits will continue to play a vital role in global nutrition, food security, and consumer satisfaction in the years to come.