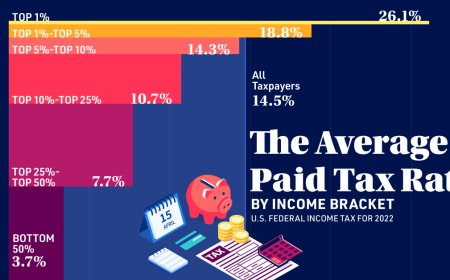
Audio Labs: Pioneering the Future of Sound Technology
Introduction
Sound is one of the most powerful and versatile forms of communication. It carries emotion, information, and intent. As technology becomes increasingly intelligent and immersive, audio has evolved from a background feature into a key element in modern design and functionality. At the forefront of this evolution are Audio Labsdedicated research and development hubs focused on pushing the boundaries of sound science and engineering.
Whether embedded within universities, tech giants, healthcare innovators, or automotive companies, Audio Labs are reshaping how we capture, analyze, synthesize, and interact with sound. These labs are where engineers, scientists, musicians, and AI researchers come together to innovate everything from speech recognition and spatial sound to hearing aids and immersive media.
What Is an Audio Lab?
An Audio Lab is a specialized facility or research group dedicated to the study, development, and application of audio technologies. It brings together multidisciplinary teams working on:
-
Acoustics and psychoacoustics
-
Digital signal processing (DSP)
-
Machine learning for audio (audio AI)
-
Speech synthesis and recognition
-
Music information retrieval
-
Hearing technologies
-
Immersive and spatial sound systems
-
Sound event detection and classification
Audio Labs can be part of academic institutions (e.g., MIT Media Lab), corporate R&D departments (e.g., Adobe AudioLab), or independent startups focused on specific audio technologies.
Key Focus Areas in Modern Audio Labs
1. Speech and Voice Processing
Modern Audio Labs are leading the charge in improving how machines understand and generate human speech. This includes:
-
Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) Converting spoken language into text.
-
Text-to-Speech (TTS) Generating natural-sounding voices from text.
-
Speaker Diarization Identifying who is speaking in a conversation.
-
Voice Cloning Replicating a specific voice with minimal samples.
Voice-based interfaces have become central to smart devices, and audio labs are ensuring they are accurate, multilingual, emotionally responsive, and privacy-conscious.
2. Spatial and 3D Audio
In the age of virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and immersive gaming, spatial audio has become a key area of innovation.
Audio Labs explore:
-
Binaural audio Simulating sound the way human ears hear it.
-
Ambisonics Encoding full-sphere surround sound for VR.
-
Dynamic sound zones Delivering personalized audio experiences in cars or shared spaces.
-
Head-related transfer functions (HRTF) Personalizing spatial sound perception.
These technologies are widely used in gaming, simulation training, and entertainment experiences like Dolby Atmos and 360 Reality Audio.
3. Audio Machine Learning and AI
Many Audio Labs specialize in machine listeningusing AI to detect patterns and insights from sound.
Applications include:
-
Sound classification Identifying specific sounds (e.g., footsteps, alarms, animal noises).
-
Audio-based diagnostics Detecting illness from coughs, speech, or breathing sounds.
-
Emotion recognition Analyzing vocal tone to infer mood.
-
Music generation Creating original music using AI models like OpenAIs Jukebox.
With audio AI, machines are becoming better at understanding the world through sound.
4. Audio Enhancement and Restoration
Audio Labs also develop tools to clean, enhance, and restore sound, especially useful in media, forensics, and accessibility.
Key developments include:
-
Noise reduction and echo cancellation
-
Audio super-resolution
-
Speech enhancement in real time
-
Audio source separation Isolating vocals or instruments from mixed tracks
These tools are critical for podcasts, streaming services, film production, and assistive technologies.
Notable Audio Labs Around the World
AudioLabs Erlangen (Germany)
One of the most respected academic-industry collaborations, this lab is a joint project of Fraunhofer IIS, the University of Erlangen-Nuremberg, and Fraunhofer Society. Known for its work in developing MP3 and AAC, the lab now explores perceptual audio coding, semantic audio, and audio-visual signal processing.
Adobe Audio Labs
This lab focuses on integrating intelligent audio features into creative tools like Adobe Audition and Premiere Pro. Key innovations include AI-powered sound enhancement, voice synthesis, and automatic transcription.
MIT Media Lab (Sound & Music Computing Group)
One of the most interdisciplinary audio labs, the group at MIT explores interactive music systems, acoustic signal processing, and sound-based human-computer interaction.
Facebook Reality Labs (Meta)
Metas lab focuses on developing audio for virtual and augmented reality. Their work includes personalized spatial audio and AI-based sound modeling for lifelike immersion in digital environments.
Applications of Audio Lab Innovations
1. Healthcare
Audio Labs are pioneering non-invasive diagnostic tools using sound analysis. For example:
-
Analyzing cough sounds to detect respiratory illnesses like COVID-19.
-
Monitoring speech patterns to diagnose neurological diseases such as Parkinsons.
-
Using voice changes to assess mental health conditions like depression.
These breakthroughs enable early detection and remote healthcare monitoring using smartphones and wearable microphones.
2. Automotive Industry
Modern vehicles, especially electric vehicles (EVs), are integrating audio systems that:
-
Generate external warning sounds for pedestrian safety.
-
Use noise-cancellation for quieter cabins.
-
Create personal sound zones using headrest speakers or speakerless audio.
-
Detect driver fatigue using vocal analysis.
Audio Labs contribute significantly to shaping these sound environments.
3. Smart Homes and Devices
Smart assistants like Alexa, Google Assistant, and Siri rely on technologies developed in Audio Labs:
-
Wake word detection
-
Far-field voice recognition
-
Personalized voice response
-
Multi-speaker interaction
These labs ensure devices are more responsive, secure, and able to function in noisy real-world conditions.
4. Media and Entertainment
From advanced mixing tools to AI-generated music, Audio Labs enable:
-
Dynamic music scoring for games and films.
-
Voice acting without actors using TTS and voice cloning.
-
Real-time audio translation and accessibility features.
These innovations enrich storytelling and enhance inclusion in digital content.
The Future of Audio Labs
As AI, sensor technology, and computing power advance, the role of Audio Labs will expand into new frontiers:
-
Multimodal systems Integrating audio with video, haptics, and biosensors for richer machine perception.
-
Context-aware audio Systems that adjust sound based on environment, user profile, and emotional state.
-
Ubiquitous sound interfaces Audio embedded in everyday objects like furniture, windows, and clothing.
-
Ethical and responsible audio AI Ensuring transparency, privacy, and fairness in voice-enabled systems.
Future Audio Labs will not only produce technology but also shape the sound ethics of the AI era, balancing innovation with user trust.
Conclusion
Audio Labs are the heart of innovation in sound technology. They fuse science, creativity, and human-centered design to improve how we interact with the worldthrough voice, music, ambient sound, and machine hearing.
From personalized audio in electric vehicles to diagnostic health tools and intelligent assistants, Audio Labs are not only solving technical problems but also transforming lives. As audio becomes a more intelligent and integrated part of our digital experience, these labs will continue to push boundaries, making sound more immersive, insightful, and meaningful.